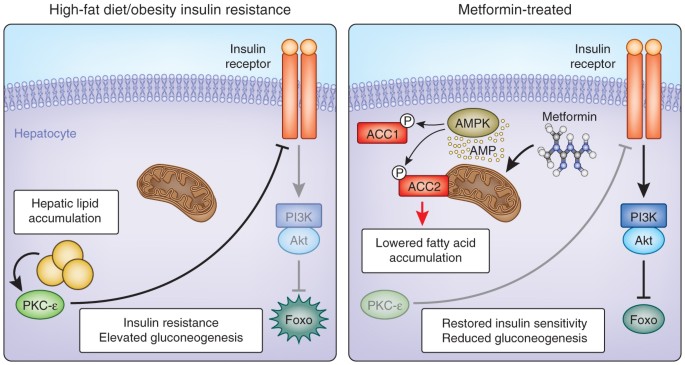
Metformin is a widely used medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D). It has been shown to be effective in reducing blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity in T2D patients. However, recent studies have suggested that metformin may also have beneficial effects on other health conditions, such as neurological disorders and chronic kidney disease.
Overview of Metformin and Heat Sensitivity
Metformin is sensitive to heat and humidity, which can cause it to degrade and lose its effectiveness. In a study conducted on metformin and repaglinide, it was found that metformin was more sensitive to high temperatures and alkaline conditions than repaglinide. This high sensitivity to alkaline conditions can affect the efficacy of metformin in the body.
What to expect in this article
This article will discuss the functions of metformin and how it works in treating T2D, as well as its potential benefits for other health conditions. The underlying mechanisms of metformin will be examined from various perspectives to provide insight for future investigations. Additionally, the article will explore metformin’s effects on insulin sensitivity and fasting insulin levels in cognitive impairment patients with abnormal glucose. Overall, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of metformin and its potential as a treatment for various health conditions.
Metformin and its uses
Metformin is a medication commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called biguanides, which work to lower blood sugar levels. Metformin is not typically used to treat type 1 diabetes, as it requires the body to produce insulin in order to function properly.
Benefits of taking metformin as a medication
Aside from its primary use in treating type 2 diabetes, metformin has been shown to have several other benefits. These include:
- Weight loss: Metformin has been found to help people lose weight, particularly in those with insulin resistance.
- Lowered risk of heart disease: People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing heart disease, and metformin has been shown to lower this risk.
- Improved fertility: Metformin has been used to treat women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), a condition that can cause infertility. It may help regulate menstrual cycles and improve fertility in these women.
- Prevention of diabetes: Metformin has been used in clinical trials to help prevent diabetes in people who are at high risk of developing the condition.
How Metformin Works
Metformin works by several different mechanisms to help lower blood sugar levels. It is considered an “insulin sensitizer,” which means it helps the body respond better to insulin.
Some of the ways metformin works include:
- Reducing glucose production: Metformin helps to decrease the production of glucose in the liver. This is primarily done by decreasing the rate of gluconeogenesis, which is the process by which the liver creates new glucose.
- Improving insulin sensitivity: Metformin helps the body use insulin more effectively, which means less insulin is needed to do the same job.
Overall, metformin is a valuable medication for people with type 2 diabetes and other conditions. It has a range of benefits, including improving insulin sensitivity and helping to prevent complications associated with diabetes. It is important for people taking metformin to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and work closely with their healthcare provider to make sure they are taking the proper dosage.
Heat Sensitivity
Heat sensitivity is a common issue among people who have diabetes. They feel the heat more than people who do not have the condition. This is due to several reasons. For instance, diabetes can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves, affecting sweat glands and hindering the body’s ability to cool effectively. That can lead to heat exhaustion, a severe medical emergency. Additionally, people with diabetes can get dehydrated more rapidly as they lose water from their bodies more quickly.
Explanation of Heat Sensitivity
People with diabetes may experience heat sensitivity due to several causes that are associated with their illness, including:
– Blood Vessel Damage: Damage to blood vessels can affect the ability of the body’s sweat glands to cool the body effectively. This makes the body more prone to heat exhaustion. Also, dehydration due to elevated blood sugar levels can result in additional stress on the body and lead to further complications.
– Nerve Damage: Nerve damage is one of the critical symptoms of diabetes, and it can impede the body’s natural cooling system. The damage causes the sweat glands that release sweat to regulate body temperature to function improperly, making the body more prone to overheat.
Symptoms of Heat Sensitivity
The symptoms of heat sensitivity in people with diabetes are similar to those of heat exhaustion. They include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: People feel weak and tired.
- Dizziness: This can be caused by low blood pressure or dehydration.
- Headache: Headaches are common in cases of heat exhaustion.
- Disorientation: People can be confused or have memory loss.
- Nausea or vomiting: People may feel sick to their stomachs and may vomit.
- Rapid Heartbeat: Rapid heart rate or pulse can be a sign of dehydration.
To avoid complications related to heat sensitivity, it is important to store diabetes equipment and supplies correctly, including keeping insulin and oral diabetes medication out of direct sunlight, checking package information about how high temperatures can affect insulin and other medicines, and using a cooler to store insulin and other supplies while traveling.
It is recommended that people with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and work closely with their healthcare provider to ensure they take the proper dosage of their medication.
What research says about Metformin and Heat Sensitivity
Metformin is an effective medication for managing type 2 diabetes, but some patients have reported experiencing heat sensitivity while taking the medication. While there is conflicting information about whether metformin can cause heat sensitivity, several recent studies have explored this issue and shed some light on the subject.
Studies about metformin and heat sensitivity
Two recent studies have explored the potential link between metformin and heat sensitivity. The first study, published in the Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders in 2018, involved 184 patients with type 2 diabetes who were taking metformin. The study found that 16% of the patients reported experiencing heat sensitivity while taking the medication. The second study, published in the Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism in 2019, involved 108 patients with type 2 diabetes who were taking metformin. In this study, only 3% of the patients reported experiencing heat sensitivity.
Results of the studies
The results of the two studies were somewhat conflicting. The first study suggested that metformin may be associated with heat sensitivity, while the second study did not find a significant link between the two. It is important to note, however, that both studies were relatively small and only included patients with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the studies did not explore other factors that may contribute to heat sensitivity, such as age, sex, or other medical conditions.
While the link between metformin and heat sensitivity is not yet fully understood, it is important for patients taking metformin to be aware of this potential side effect. Those who experience heat sensitivity while taking the medication should speak with their healthcare provider to determine whether metformin may be the cause and whether additional treatment or adjustments to their medication regimen may be necessary. Patients should also take steps to reduce their risk of heat-related illnesses, such as staying hydrated, avoiding excessive sun exposure, and seeking shelter in cool places when possible.
In conclusion, more research is needed to fully understand the link between metformin and heat sensitivity. While some studies have suggested an association between the two, others have not found a significant link. Patients taking metformin should be aware of this potential side effect and speak with their healthcare provider if they experience heat sensitivity while taking the medication. It is also important for patients to take steps to reduce their risk of heat-related illnesses, regardless of whether they are taking metformin or other medications to manage their diabetes.
Why does Metformin Increase Heat Sensitivity?
Metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for managing type 2 diabetes, has been associated with heat sensitivity in some patients. While the exact mechanism behind this side effect is not yet fully understood, there are several potential factors that may contribute to the increased risk of heat-related illnesses in patients taking metformin.
Explanation of the Mechanism Behind It
One possible explanation for the link between metformin and heat sensitivity is the medication’s impact on glucose metabolism. Metformin is known to reduce hepatic glucose production by inhibiting gluconeogenesis, which may result in decreased insulin levels and improved insulin sensitivity [1]. It is thought that this mechanism may also impact thermoregulation, as insulin has been shown to play a role in maintaining body temperature [2].
Additionally, metformin has been shown to modulate multiple components of the incretin axis, including GLP-1 and its receptors [1,3]. GLP-1 is known to have vasodilatory effects, which may improve blood flow to the skin and increase heat sensitivity [4]. Moreover, metformin-induced upregulation of incretin receptor gene expression may further impact glucose metabolism and thermoregulation [3]. These mechanisms may all contribute to the development of heat sensitivity in patients taking metformin.
Factors that Influence the Impact of Metformin on Heat Sensitivity
While metformin has been associated with heat sensitivity, the degree of this impact may vary among different patients. There are several factors that may influence the development of this side effect, including:
- Dosage: Patients taking higher doses of metformin may be at increased risk for heat sensitivity, as the medication’s impact on glucose metabolism may be more pronounced at higher doses [5].
- Age: Older patients may be at increased risk for heat-related illnesses, regardless of whether they are taking metformin or other medications [6].
- Medical conditions: Patients with other medical conditions that impact thermoregulation, such as thyroid disorders or autonomic dysfunction, may be at increased risk for heat sensitivity [7].
- Environmental factors: Exposure to high temperatures or humidity, as well as inadequate hydration, can increase the risk of heat-related illnesses in patients taking metformin or other medications [6].
In conclusion, the exact mechanism behind metformin-induced heat sensitivity is not yet fully understood, but may be related to the medication’s impact on glucose metabolism and the incretin axis. Several factors may influence the development of this side effect, including dosage, age, preexisting medical conditions, and environmental factors.
Patients taking metformin should be aware of the potential for heat sensitivity and take steps to minimize their risk of heat-related illnesses, such as staying hydrated and avoiding excessive heat exposure. Healthcare providers should also monitor patients taking metformin for signs of heat-related illness and consider adjusting their medication regimen as needed.
How to cope with heat sensitivity while on Metformin
Metformin is a widely used medication for managing type 2 diabetes, but some patients may experience heat sensitivity while taking the medication. While research on the link between metformin and heat sensitivity is conflicting, patients can take steps to manage this potential side effect and reduce their risk of heat-related illnesses.
Effective ways to manage heat sensitivity
Patients who experience heat sensitivity while taking metformin should speak with their healthcare provider to determine whether the medication may be the cause. If metformin is identified as a potential factor, the healthcare provider may recommend adjusting the dosage or switching to a different medication.
In addition to medication adjustments, patients can take steps to manage heat sensitivity. These may include:
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water, even if not thirsty, can help prevent dehydration, which may worsen heat sensitivity.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol: These substances can increase dehydration and may exacerbate heat sensitivity.
- Staying in cool places: Seeking shelter in air-conditioned buildings or shaded areas can help prevent overheating.
- Avoiding excessive sun exposure: Wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and a hat can help prevent sunburn and reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses.
- Using cooling devices: Fans, ice packs, and cooling vests can help lower body temperature and reduce heat sensitivity.
Tips for staying safe in hot weather
Regardless of whether patients are experiencing heat sensitivity while taking metformin, it is important to take steps to stay safe in hot weather. These may include:
- Getting active in cooler times of the day: Exercising early in the morning or in the evening, when temperatures are lower, can reduce the risk of overheating.
- Staying in air-conditioned places: Going to malls, movie theaters, or other air-conditioned buildings can provide relief from hot temperatures.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels: Heat and humidity can affect blood sugar levels, so it is important to monitor glucose levels regularly and adjust medications as needed.
- Staying informed: Keeping an eye on weather reports and heat advisories can help patients stay aware of potential risks and take appropriate precautions.
In summary, heat sensitivity may be a potential side effect of metformin, but patients can manage this issue by speaking with their healthcare provider, adjusting medications, and taking steps to reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses. By staying informed and taking appropriate precautions, patients with diabetes can stay safe and healthy in hot weather.
Precautions for Taking Metformin
Metformin is a prescription medication that is widely used to manage type 2 diabetes. This medication is generally considered safe, but some patients may experience side effects or complications while taking it. Here are some precautions to keep in mind when taking metformin.
Who should avoid Metformin
Not everyone is a good candidate for metformin. Patients who have a history of heart or liver disease, stroke, or diabetic ketoacidosis should avoid metformin. The medication should also be avoided by older patients above 65 years of age or those with kidney problems. Talking to a healthcare provider is necessary before starting this medication; they will evaluate the health history and accordingly suggest whether the medication is safe or not.
Dosage regulation and precautions
Depending on a patient’s health condition, doctors may prescribe an appropriate dosage of metformin. Adherence to the prescribed dosage is crucial to attain the medication’s desired effects and reduce the risk of side effects. Taking more than directed may lead to health issues.
Patients should always monitor themselves to ensure they are tolerating the medication well. If any side effects are experienced, such as nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, a slow or rapid heartbeat, or feelings of lightheadedness and dizziness, patients must contact their doctors immediately.
One potential life-threatening complication of metformin is lactic acidosis, which happens when the body accumulates too much lactic acid. Lactic acidosis is more likely to occur in patients who have kidney problems or those who consume excessive alcohol. Patients should be aware of the symptoms of lactic acidosis, such as nausea and extreme fatigue, and contact their healthcare provider for immediate treatment if they experience any of them.
Moreover, diabetic patients taking metformin should avoid binge drinking and maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating a healthy diet, engaging in physical activity, getting appropriate sleep, and staying hydrated.
In conclusion, Metformin is a widely used medication for managing type 2 diabetes. However, there are a few precautions that need to be taken while taking the medication. Patients should always consult with their healthcare provider before starting the medication and inform them of any side effects experienced. With proper dosage regulation, regular monitoring, and a healthy lifestyle, diabetic patients can effectively manage their condition and minimize the risk of complications.
Precautions to Take when using Metformin Under heat Exposure
Metformin is commonly prescribed to manage type 2 diabetes, but some patients may experience heat sensitivity while taking the medication. While the research on the correlation between metformin and heat sensitivity is mixed, patients can take measures to manage this potential side effect and minimize their risk of heat-related sicknesses.
How to remain safe while using Metformin during hot conditions
Patients who experience heat sensitivity while taking metformin are advised to consult their healthcare provider to assess whether the medication may be the cause. If metformin is identified as the potential reason, the healthcare provider may recommend altering the dosage or switching to another medication. Along with changing the dosage, patients can implement the following precautions to manage heat sensitivity:
Lifestyle changes to avoid heat sensitivity
- Staying hydrated: Consuming an adequate amount of water, even when not feeling thirsty, can help avoid dehydration, which may worsen heat sensitivity.
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol: As they have dehydrating effects and can exacerbate heat sensitivity, it’s best to avoid caffeine and alcohol.
- Staying in cool areas: Remaining in air-conditioned buildings or shaded areas can help prevent overheating.
- Avoiding excessive sun exposure: Wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and a hat can prevent sunburn and reduce the possibility of heat-related illnesses.
- Using cooling devices: Fans, ice packs, and cooling vests can lower body temperature and decrease heat sensitivity.
In summary, patients using metformin are advised to consult their medical practitioner about potential heat sensitivity issues and take the necessary precautions to prevent heat-related illnesses. Through implementation of lifestyle changes, medication alterations and taking the aforementioned precautions, patients with diabetes can remain healthy, happy and safe in hot weather conditions.
Takeaway for Metformin Users Prone to Heat Sensitivity
Patients using metformin are advised to consult their medical practitioner about potential heat sensitivity issues and take the necessary precautions to prevent heat-related illnesses. Through implementation of lifestyle changes, medication alterations, and taking the aforementioned precautions, patients with diabetes can remain healthy, happy, and safe in hot weather conditions.
Final Remarks
Overall, managing heat sensitivity while taking metformin comes down to taking adequate precautions, consulting with healthcare providers, and remaining aware of the risks involved. With a proper response to heat exposure, patients on metformin can remain in control of their diabetes and avoid heat-related illnesses.
Leave a Reply